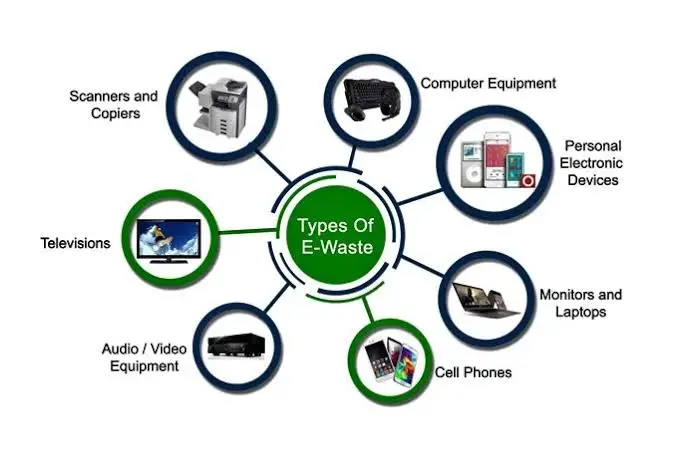
Top 10 Electronic Waste Sources in India
In the midst of India’s rapid technological advancement, a parallel challenge looms large – the surge in electronic waste. With a burgeoning middle class and increasing access to electronic gadgets, the country finds itself at the crossroads of progress and sustainability. As the digital revolution sweeps across the nation, the question of responsible dispose land management of electronic waste has never been more pertinent.
This article delves into the intricate web of electronic waste sources in India, shedding light on the multifaceted aspects that contribute to this environmental predicament. From obsolete smartphones to outmoded laptops, the sheer volume of discarded electronics paints a vivid picture of the urgency to address this issue. Join us as we explore the origins, trends, and potential solutions to mitigate the impact of electronic waste on India’s environment and public health.
1. Obsolete Personal Computers and Laptops
As technology advances at an exponential rate, personal computers and laptops quickly become outdated. This leads to a significant influx of e- waste as users replace their old devices with newer models. Components such as processors, motherboards, and monitors contribute to the growing e-waste stream.
Example: The release of faster processors and enhanced graphics cards prompts many users to upgrade their computers, resulting in older systems being discarded.
2. Outdated Mobile Phones and Smartphones
In the era of constant innovation, mobile phones and smartphones have a short lifespan. Rapid developments in mobile technology encourage consumers to replace their devices with newer, more advanced models, generating a substantial amount of e- waste.
Example : When a new smartphone with enhanced features and capabilities hits the market, consumers tend to trade in their older models, contributing to the e-waste surge.
3. Defunct Televisions and Monitors
With the transition from cathode ray tube (CRT) to flat-panel displays, outdated televisions and monitors are frequently disposed of. The presence of hazardous materials in CRT displays poses a particular environmental concern when not properly managed.
–Example : As LED and LCD technologies become standard, older CRT televisions and monitors are rapidly phased out, adding to the e- waste stream.
4. Discarded Printers and Scanners
Rapid advancements in printing technology render older printers and scanners obsolete. Their complex internal components, including toner cartridges and electronic circuits, contribute significantly to electronic waste.
As businesses and households upgrade to more efficient and feature-rich printing equipment, older models find their way into the e-waste stream.
5. Abandoned Consumer Electronics
A wide range of consumer electronics, such as DVD players, gaming consoles, and audio equipment, contribute to the electronic waste stream when they are no longer in use. These devices contain various materials, including plastics, metals, and potentially hazardous components like batteries.
Example :With the rise of streaming services, many households discard older DVD players and gaming consoles, leading to electronic waste accumulation.
6. Expired Batteries
Batteries, whether from portable electronic devices or larger equipment, represent a significant source of electronic waste. Over time, batteries lose their capacity to hold a charge, necessitating replacement.
Rechargeable batteries in laptops, mobile phones, and other devices gradually degrade, prompting users to purchase new ones and dispose of the old ones.
7. Dismantled Networking Equipment
Networking equipment like routers, switches, and modems often become outdated due to evolving technology standards. These devices contain valuable metals and components that contribute to electronic waste when discarded.
The transition from older networking protocols to newer, more efficient standards prompts the replacement of networking equipment, resulting in electronic waste.
8. Unusable Kitchen Appliances
Kitchen appliances like microwaves, blenders, and coffee makers contain electronic components that may fail over time. When these devices are beyond repair, they are often discarded, contributing to the electronic waste stream.
When a microwave’s electronic control panel malfunctions and the cost of repair outweighs replacement, it is likely to be disposed of, adding to electronic waste.
9. End-of-Life Entertainment Systems
Home entertainment systems, including stereos, DVD players, and gaming consoles, become obsolete as newer and more advanced models enter the market. The disposal of these devices leads to electronic waste accumulation.
Example :With the advent of high-definition and smart TVs, older entertainment systems are frequently replaced, contributing to the e-waste problem.
10. Broken or Expired Home Appliances
Large home appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners contain electronic components for control and automation. When these appliances reach the end of their operational life, they become a source of electronic waste.
Example :A refrigerator with a malfunctioning compressor or thermostat may be beyond repair, necessitating disposal and contributing to the electronic waste stream.
These diverse sources collectively underline the pressing need for effective electronic waste management strategies to mitigate environmental and public health impacts.
Environmental Impact of Electronic Waste
Here are 10 points explaining the impacts of electronic waste and environmental pollution:
Toxic Components
Electronic waste, or e-waste, contains hazardous materials like lead, mercury, cadmium, and flame retardants. When improperly disposed of, these substances can seep into the soil and water, contaminating the environment.
Landfill Leaching
When e-waste ends up in landfills, rainwater can percolate through the waste, picking up toxins and carrying them into the soil, potentially contaminating groundwater sources and nearby ecosystems.
Air Pollution
Burning e-waste in open dumps or informal recycling operations releases harmful chemicals into the air. This includes dioxins, furans, and other pollutants, contributing to air pollution.
Water Contamination
E-waste dumping and inadequate disposal methods can lead to the release of toxic substances into water bodies. This contamination can harm aquatic life and impact human health if the water is used for drinking or irrigation.
Read Also : 5g Effects on Environment and Human
Soil Degradation
Toxic chemicals from e-waste can accumulate in soil, affecting plant growth and potentially entering the food chain. This can lead to health risks for both humans and animals.
Health Risks
Exposure to the hazardous materials in e-waste can lead to a range of health issues, including respiratory problems, skin conditions, and damage to vital organs. This is especially concerning for workers in the informal recycling sector.
Global Impact
E-waste is often exported to developing countries, where informal recycling practices are prevalent. This can lead to severe environmental and health consequences in these regions.
Resource Depletion
Electronics contain valuable materials like gold, silver, and rare earth metals. Inadequate recycling means that these resources are lost, leading to increased mining activities, which have their own environmental impact.
Read Also : Deepfake Bots Explained
Energy Consumption
Manufacturing electronics requires a significant amount of energy. When e-waste is not properly recycled, it leads to increased demand for new products, further contributing to energy consumption and associated emissions.
Regulatory Challenges
In many parts of the world, there is a lack of effective regulation and enforcement regarding the proper disposal and recycling of e-waste. This allows for illegal and environmentally harmful practices to persist.
In summary, electronic waste poses a serious threat to the environment through the release of toxic substances, contamination of air, water, and soil, and the depletion of valuable resources. Proper disposal, recycling, and responsible consumer behavior are crucial in mitigating these environmental impacts.
Electronic Waste Disposal in Chennai
Chennai, a bustling metropolis in India, grapples with the challenge of electronic waste disposal. The city, known for its burgeoning IT industry and rising consumer electronics usage, faces a mounting e-waste crisis. The disposal process involves collecting, segregating, and recycling electronic items like computers, mobile phones, and appliances, as well as ensuring the safe disposal of hazardous components.
Several initiatives have been undertaken by the local government and non-profit organizations to address this issue. Authorized e-waste collection centers have been established, aiming to promote responsible disposal practices. These centers facilitate the segregation of electronic items based on their components, directing them to proper recycling facilities.
Additionally, awareness campaigns and educational programs have been conducted to inform residents about the hazards of improper e-waste disposal and to encourage them to utilize designated collection points. Chennai’s civic authorities have also collaborated with recycling companies and NGOs to implement sustainable and eco-friendly methods for processing e-waste.
However, challenges persist, including the need for more extensive public awareness efforts, enhanced enforcement of regulations, and increased accessibility to disposal facilities, especially in densely populated areas. The issue of informal recycling, often conducted under hazardous conditions, remains a concern.
Recycling of Electronis Waste
Recycling e-waste is crucial for minimizing its environmental impact. Here’s a simplified guide on how e-waste recycling can be done:
Collection
Start by collecting electronic devices that are no longer in use. This could include old computers, laptops, phones, printers, and appliances.
Segregation
Separate items into categories like computers, mobile phones, batteries, cables, and other components. This helps in proper handling and recycling of each type of material.
Data Wiping
Before recycling, ensure that all personal data is wiped from devices. This is especially important for smartphones and computers.
Authorized Recycler
Identify and contact an authorized e-waste recycling facility. They have the expertise and equipment needed for safe processing.
Transportation
Deliver the e-waste to the recycling facility or use designated drop-off points. Some companies provide pickup services for larger quantities.
Dismantling
At the facility, trained technicians will disassemble the items. They extract valuable materials like metals, plastics, and circuit boards.
Material Processing
Metals
Ferrous (iron-based) and non-ferrous metals are separated and sent for smelting and refining.
Plastics
Plastic components are sorted, cleaned, and then melted down for reuse.
Circuit Boards
These are processed to extract precious metals like gold, silver, and copper.
Hazardous Materials
Hazardous components like batteries and mercury-containing bulbs are treated separately to prevent environmental contamination.
Recovery and Reuse
Once materials are processed, they are often sold to manufacturers to produce new electronics or other products.
Environmentally Safe Disposal
Any residual waste that cannot be recycled is disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner.
Remember, it’s important to use authorized and certified e-waste recyclers to ensure proper handling and disposal. Avoid informal recycling methods, as they can have serious health and environmental consequences. By recycling e-waste, we conserve resources, reduce pollution, and contribute to a more sustainable future.

2 thoughts on “Electronic Waste: Sources, Environmental Impacts and Recycling in India”