Unlocking the Mysteries of the Human Brain with Lab-Grown Organoids
The human brain, a complex and elusive organ, has long been a subject of fascination and study. Despite advancements in technology, understanding the full scope of its functions and disorders remains a challenge. Enter the revolutionary concept of cerebral organoids: lab-grown mini-cerebral that could pave the way for groundbreaking research in neuroscience.
The Need for Cerebral Organoids
Neuroscientists have traditionally relied on autopsies, animal models, and imaging techniques to study the cerebrals. However, these methods fall short when it comes to observing the cerebral in action and understanding complex conditions like Alzheimer’s and schizophrenia. Brain organoids offer a promising solution by simulating human cerebral tissue outside of an organism, allowing for direct observation and experimentation.
Read Also : Optogenetic Pain Reduction
From Skin Cells to Brain Tissue
One of the most remarkable aspects of these organoids is their origin from undifferentiated stem cells, which can be derived from a simple skin sample. This means scientists can create cerebral tissue that genetically matches individuals with specific conditions, providing personalized insights into neurological diseases.
The Challenge of Growing Brain Organoids
The journey to successfully grow these organoids was not straightforward. The breakthrough came in 2013 when the optimal mix of nutrients to encourage stem cells to develop into neural tissue was discovered. This development made the process of growing cerebral organoids much more accessible, paving the way for widespread research applications.
Read Also : Is NASA receiving alien signal from 35 years
The Growth Process: Simulating Development
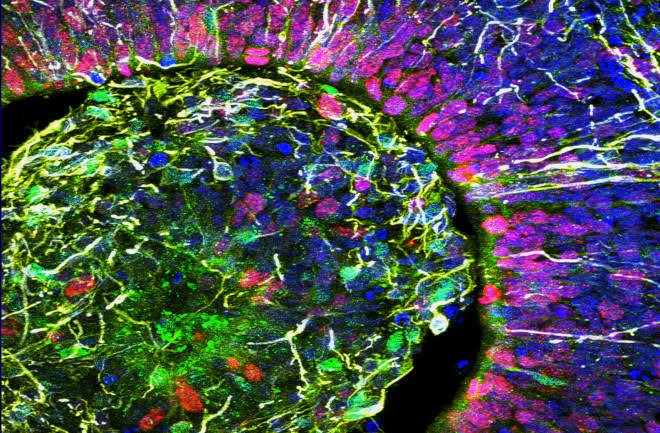
Growing a brain organoid is akin to planting a seed and nurturing it to growth. By providing a gel to simulate embryonic tissue, maintaining the right temperature, and introducing motion to mimic blood flow, scientists can grow organoids that undergo stages of cerebral development. This process offers invaluable insights into how human brains evolve and differentiate from other species.
Ethical Considerations and Limitations
Despite their potential, the organoids raise ethical questions, particularly concerning the possibility of consciousness. However, due to their lack of organization and size, organoids cannot think or develop consciousness like human brains. They lack the complex network and environmental interactions necessary for cognitive functions, limiting their size and scope but not their utility as research tools.
Read Also : Human Xenomorph Hybrid
A Tool for Understanding and Discovery
While they may not replicate the full capabilities of the human cerebral organoids are unparalleled in their potential to advance our understanding of development and disease. They hold the promise of unlocking the secrets of neurological conditions, contributing to the development of treatments, and possibly answering profound questions about what makes us human.
In conclusion, brain organoids represent a significant leap forward in neuroscience research. By providing a novel way to study the intricacies of the human cerebral, they offer hope for unraveling the mysteries of complex brain disorders and advancing our understanding of human cognition and development.